20, June 2024
MYTH #1
Myth: A comprehensive TPRM program is only essential for organizations with thousands of third parties.
Reality: Even a single vulnerability in your third-party ecosystem — extending to fourth and nth parties — can jeopardize your entire supply chain. You are only as secure as your weakest link
How to Address It: Implement a “fit-for-purpose” TPRM program to right-size your efforts and resources and address the risk of an evolving threat landscape.
MYTH #2
Myth: All third parties present the same level of risk
Reality: Third parties differ significantly in risk exposure, data sensitivity, and operational criticality. A one-size-fits-all approach is ineffective
How to Address It: Implement a risk-based approach for a more effective and efficient TPRM program
MYTH #3
Myth: More assessments lead to a stronger TPRM program.
Reality: Many organizations over-engineer TPRM assessments without realizing actual risk reduction.
How to Address It: Optimize the assessments by adopting a combination of modernized and intelligent automation techniques for risk identification
MYTH #4
Myth: Traditional risk assessments are an essential pillar of effective TPRM.
Reality: In risk posture, the likelihood and impact of an incident are dynamic through a third-party lifecycle. Over-reliance on a one-time snapshot gives the organization a false sense of security.
How to Address It: Adopt a data-driven algorithmic approach combining internal and external parameters to ensure ongoing visibility and reduce efforts and reliance on manual risk assessments
MYTH #5
Myth: Rigorous risk assessments lead to a robust TPRM
Reality: Risk mitigation is often overlooked, while risk identification gets hyper attention in the TPRM lifecycle
How to Address It: Focus more on ‘act’ than ‘assess’ to reduce the overall risk by utilizing previous issues to address fundamental root causes.
MYTH #6
Myth: TPRM is independent of procurement, IT, or information security
Reality: Risk mitigation is often overlooked, while risk identification gets hyper attention in the TPRM lifecycle.
How to Address It: Identify clear RACI, including the level of involvement throughout the third-party lifecycle management, and use hyper-automation to reduce
coordination debt.
MYTH #7
Myth: Only technology third parties are relevant for TPRM.
Reality: While cybersecurity is a significant concern, TPRM involves compliance, operational risk, financialstability, legal risks, and service continuity
How to Address It:Consider all significant risk areas (relevant to your organization) and the 100% third-party ecosystem while defining the building blocks of your TPRM program.
TPRM IN-A-BOX
At Uniqus, we specialize in helping you establish, manage, and optimize a modernized, fit-for-purpose Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) program.
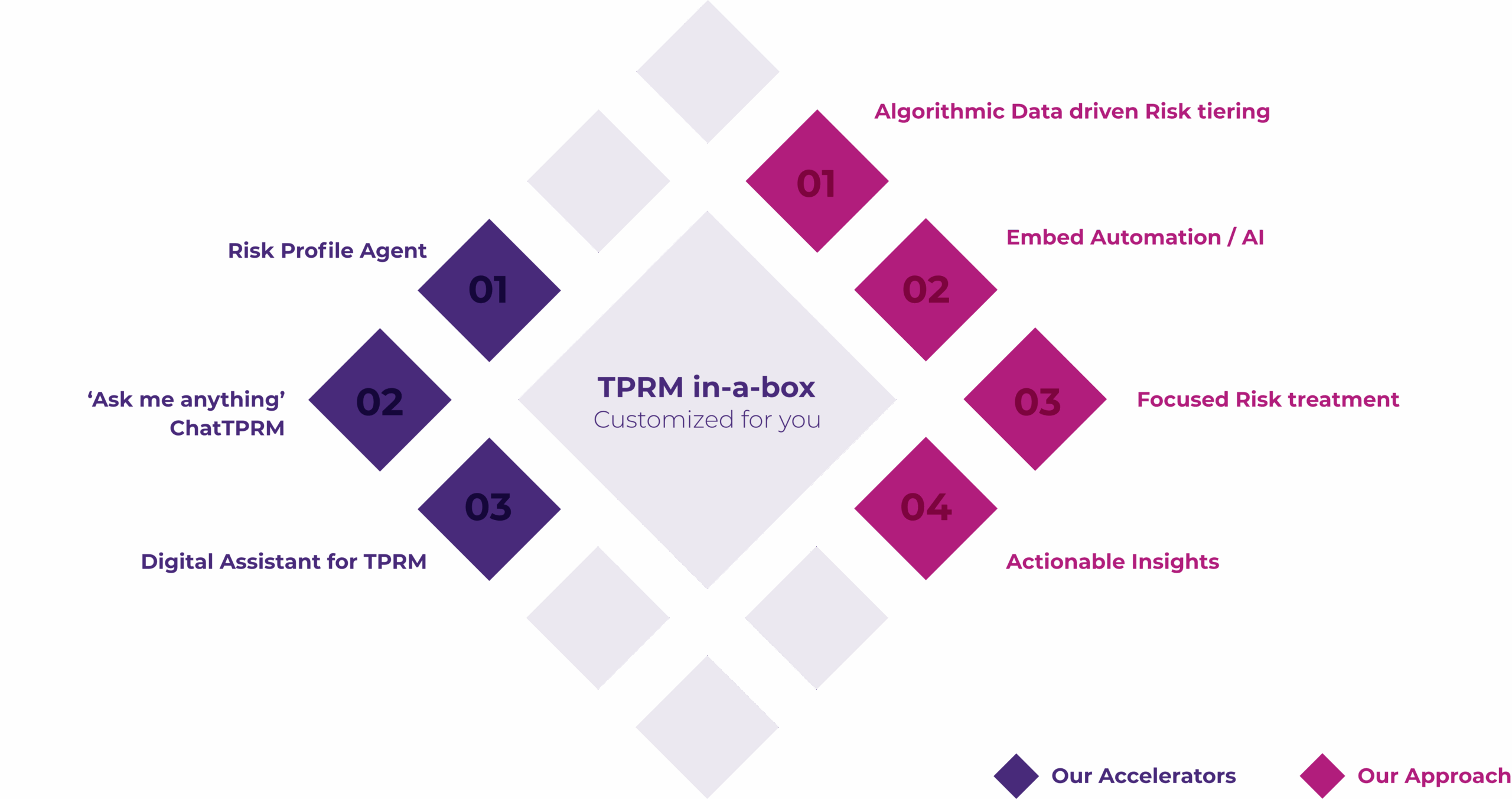
Foundational Pillars
Visibility: 100% coverage for the third-party ecosystem
Efficiency: 40% efficiency improvement in the first
Consistency: Improved consistency across the life-cycle
Risk reduction: Proactive risk reduction for early interventions
Related
Early Impressions
Elevating TPRM to a strategic risk and boardroom priority
SAMA Vision 2030: Pioneering the Future of Saudi Arabia’s Financial Landscape The Saudi Central Bank (SAMA) Vision 2030 is a strategic pillar aligned with the Kingdom’s broader Vision 2030, driving a digitally empowered, resilient, and globally competitive financial sector. As...
Newsletter
ESG Corner- June 2025
In the news This section focuses on key developments globally, in the U.S., India, and the Middle East. It dissects the most recent news and analyzes its potential to influence regional landscapes, businesses, and consumers. Uniqus provides insights into recent...
Uniqus Point of View
IFRS 18 – Practical considerations for Banking institutions in the Middle East
Executive Summary IFRS 18, Presentation and Disclosure in Financial Statements, issued by the IASB, substantially changes the structure and presentation of financial statements. It brings a renewed focus on amanagement-relevant metrics and investor-aligned disclosures. The key concepts introduced under IFRS...




